7��8��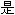 �����̸��ְص�Grimbald
�����̸��ְص�Grimbald �����գ�ʥ���ְͶ��£������ķ�߶��£���820��7��8��901��7��8�գ�
�����գ�ʥ���ְͶ��£������ķ�߶��£���820��7��8��901��7��8�գ� һ
һ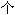 9����
9����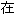 ʥ����������
ʥ���������� ʥ��̹��Ժ
ʥ��̹��Ժ
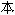 ��
�� ɮ�¡�
ɮ�¡�
������ʷȷ�����˻��ɣ�������ķ�͵� ��ƽ����¼
��ƽ����¼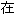 �������У�����
�������У����� ��Ҫ������Դ����Ϊʥ����ķ�͵�
��Ҫ������Դ����Ϊʥ����ķ�͵� ά��·������������ά��·���������������¹���
ά��·������������ά��·���������������¹���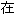 ��ͳ��
��ͳ��
 ��
��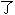 ����ķ�Ͷ��£�
����ķ�Ͷ��£�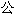 Ԫ892�����ң�����ķ�͵���������
Ԫ892�����ң�����ķ�͵���������
 ������������
������������ ��Ӣ��������ķ�͵�
��Ӣ��������ķ�͵� ������������
������������ Ӣ����͢Э����������ѧ�о�
Ӣ����͢Э����������ѧ�о� ѧ��֮һ����Ҳ
ѧ��֮һ����Ҳ �������
�������
 ѧ��֮һΰ
ѧ��֮һΰ
 ����ػ�������������
����ػ�������������
 ���Ӹ���ķ�Ͷ��������
���Ӹ���ķ�Ͷ��������
 ����������
����������
 ��������ܾ�
��������ܾ� ��
��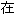 ���װͶ���
���װͶ��� һ���У����ܾ�
һ���У����ܾ�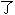 �������¹�����
�������¹�����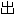
 �������ز���
�������ز���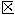
 ���飬����������
���飬���������� ������������Ϊһ
������������Ϊһ ��δ����
��δ���� ��Ժ��
��Ժ�� ��˹��
��˹�� ��ԺԺ
��ԺԺ ��
�� �³�˹�أ����»�������[1]����ķ�߶���
�³�˹�أ����»�������[1]����ķ�߶��� 901��7��8��
901��7��8��
 ��˹��ȥ����������Ϊʥͽ�
��˹��ȥ����������Ϊʥͽ� ���ߣ�����һЩ��̳��������������
���ߣ�����һЩ��̳�������������� ��
��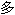 ţ�������
ţ�������
Although of dubious historical accuracy, the life of Grimbald was recorded in several volumes, of which the main source is referred to as the Vita Prima of St. Grimbaldi. According to the Vita Prima, King Alfred met Grimbald before his reign, and after his coronation invited Grimbald to England around 892. Invited for his linguistic and compositional ability, Grimbald was one of several scholars who had been invited to the English court by Alfred to assist him in his literary pursuits,[2] and was among the most prominent.[3] In fact, in the Introduction of his translation of Gregory the Great's Pastoral Care, Alfred mentions the help he received from Grimbald in composing Latin. Although it is said that during Grimbald's life he refused King Alfred's offer of appointment to the see of Canterbury,[2] after Alfred's death he accepted appointment as abbot to a yet unbuilt monastery, New Minster, in Winchester by King Edward.[1] Grimwald died at New Minster on 8 July 901.He was venerated as a saint and confessor, and some altars were dedicated to him. He also figures in a number of legendary tales of Oxford.[4]
 �����̸��ְص�Grimbald
�����̸��ְص�Grimbald �����գ�ʥ���ְͶ��£������ķ�߶��£���820��7��8��901��7��8�գ�
�����գ�ʥ���ְͶ��£������ķ�߶��£���820��7��8��901��7��8�գ� һ
һ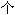 9����
9����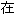 ʥ����������
ʥ���������� ʥ��̹��Ժ
ʥ��̹��Ժ
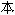 ��
�� ɮ�¡�
ɮ�¡�������ʷȷ�����˻��ɣ�������ķ�͵�
 ��ƽ����¼
��ƽ����¼ �������У�����
�������У����� ��Ҫ������Դ����Ϊʥ����ķ�͵�
��Ҫ������Դ����Ϊʥ����ķ�͵� ά��·������������ά��·���������������¹���
ά��·������������ά��·���������������¹��� ��ͳ��
��ͳ��
 ��
�� ����ķ�Ͷ��£�
����ķ�Ͷ��£� Ԫ892�����ң�����ķ�͵���������
Ԫ892�����ң�����ķ�͵���������
 ������������
������������ ��Ӣ��������ķ�͵�
��Ӣ��������ķ�͵� ������������
������������ Ӣ����͢Э����������ѧ�о�
Ӣ����͢Э����������ѧ�о� ѧ��֮һ����Ҳ
ѧ��֮һ����Ҳ �������
�������
 ѧ��֮һΰ
ѧ��֮һΰ
 ����ػ�������������
����ػ�������������
 ���Ӹ���ķ�Ͷ��������
���Ӹ���ķ�Ͷ��������
 ����������
����������
 ��������ܾ�
��������ܾ� ��
�� ���װͶ���
���װͶ��� һ���У����ܾ�
һ���У����ܾ� �������¹�����
�������¹�����
 �������ز���
�������ز���
 ���飬����������
���飬���������� ������������Ϊһ
������������Ϊһ ��δ����
��δ���� ��Ժ��
��Ժ�� ��˹��
��˹�� ��ԺԺ
��ԺԺ ��
��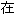 �³�˹�أ����»�������[1]����ķ�߶���
�³�˹�أ����»�������[1]����ķ�߶���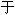 901��7��8��
901��7��8��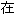
 ��˹��ȥ����������Ϊʥͽ�
��˹��ȥ����������Ϊʥͽ�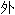 ���ߣ�����һЩ��̳��������������
���ߣ�����һЩ��̳�������������� ��
�� ţ�������
ţ�������Although of dubious historical accuracy, the life of Grimbald was recorded in several volumes, of which the main source is referred to as the Vita Prima of St. Grimbaldi. According to the Vita Prima, King Alfred met Grimbald before his reign, and after his coronation invited Grimbald to England around 892. Invited for his linguistic and compositional ability, Grimbald was one of several scholars who had been invited to the English court by Alfred to assist him in his literary pursuits,[2] and was among the most prominent.[3] In fact, in the Introduction of his translation of Gregory the Great's Pastoral Care, Alfred mentions the help he received from Grimbald in composing Latin. Although it is said that during Grimbald's life he refused King Alfred's offer of appointment to the see of Canterbury,[2] after Alfred's death he accepted appointment as abbot to a yet unbuilt monastery, New Minster, in Winchester by King Edward.[1] Grimwald died at New Minster on 8 July 901.He was venerated as a saint and confessor, and some altars were dedicated to him. He also figures in a number of legendary tales of Oxford.[4]


